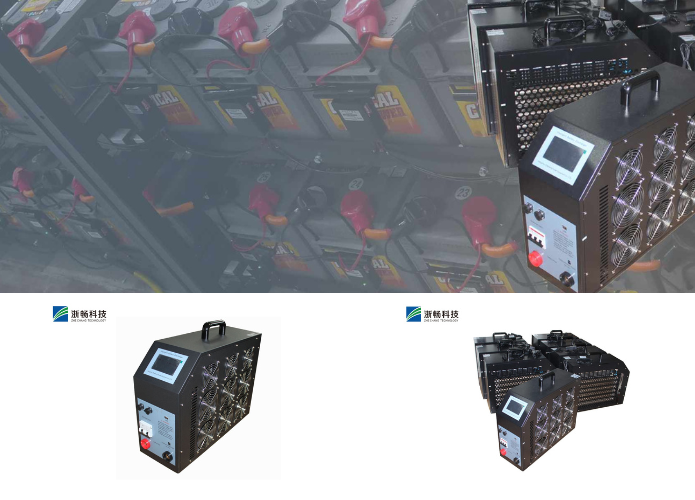
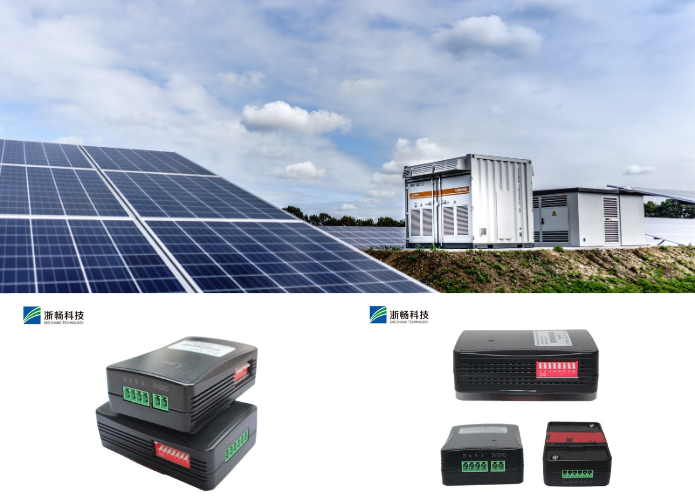
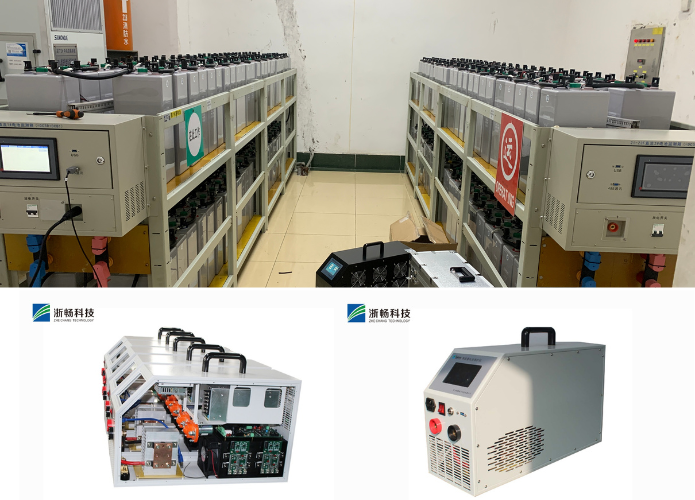
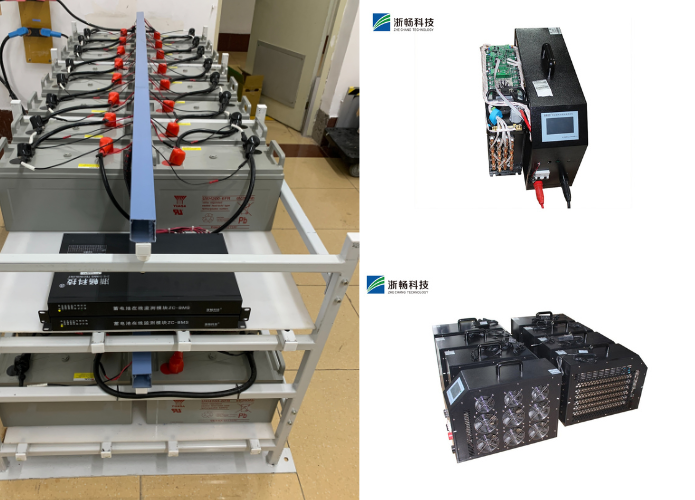
What is DC Electronic Load
In the realm of electronics testing and development, one critical tool often goes unnoticed by the general public but is indispensable to engineers and technicians—the DC electronic load. This versatile device plays a vital role in testing, evaluating, and ensuring the reliability of power supplies, batteries, and other electrical components. In this blog, we’ll dive deep into answering the question, "What is DC electronic load?" and explore its importance, types, applications, and how to select the right one for your needs.

Understanding DC Electronic Load
So, what is DC electronic load? In simple terms, it is a device designed to simulate a variety of electrical loads. By electronically controlling the amount of current or voltage drawn from a power source, it allows users to evaluate the performance and behavior of the source under different conditions. Unlike traditional resistive loads, DC electronic loads offer programmable settings, real-time measurements, and precise control, making them a cornerstone in testing environments.
Breaking Down the Definition
To fully grasp what is DC electronic load, it helps to break the concept into simpler elements:
- Programmable Load Simulation: Unlike fixed resistors, a DC electronic load can emulate different electrical loads dynamically, such as a steady current, fluctuating voltage, or specific power levels.
- Controlled Testing: Engineers can precisely control the parameters to stress-test devices, helping identify performance limits and reliability under various conditions.
- Real-Time Feedback: Most modern DC electronic loads provide real-time data visualization, ensuring accurate and detailed insights during testing.
Key Components of a DC Electronic Load
To better understand what is DC electronic load, let’s break down its primary components:
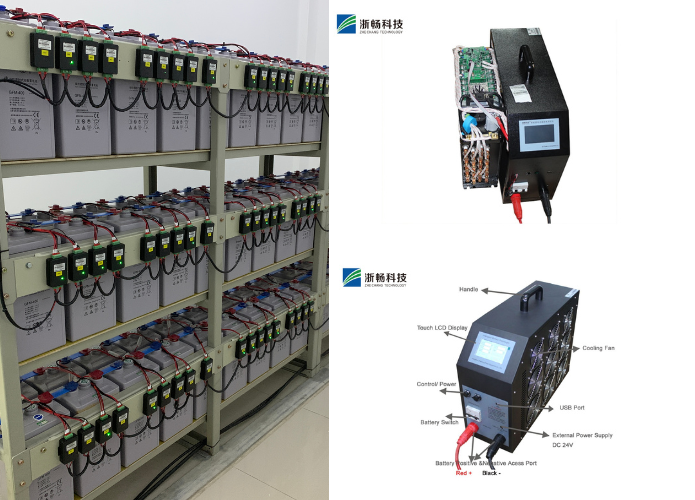
- Load Input Terminals: These are the connection points for the device under test (DUT), such as batteries or power supplies. Proper connection ensures accurate and safe testing.
- Control Circuitry: This enables users to program the load’s behavior, including constant current, voltage, resistance, or power modes. Advanced control systems allow for more complex test setups and automation.
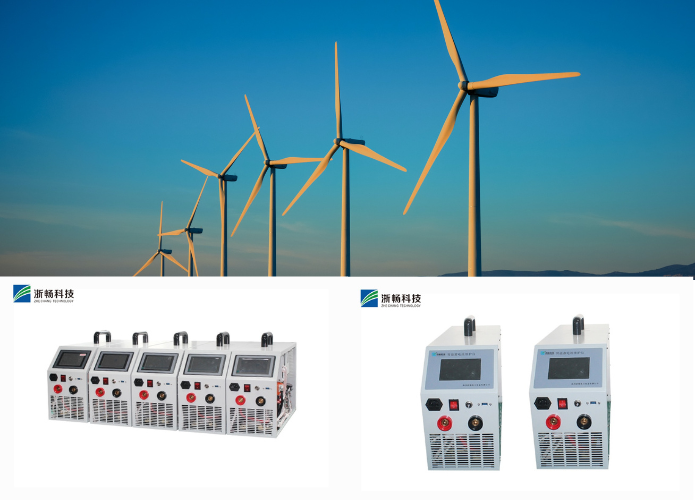
- Power Dissipation Unit: Excess energy drawn from the DUT is dissipated as heat, often managed with cooling systems like fans or heatsinks to maintain safe operating temperatures.
- Display and Monitoring Tools: Modern DC electronic loads feature digital interfaces to display parameters like current, voltage, power, and resistance in real time. Advanced models include touchscreens and data logging capabilities.
- Safety Features: Built-in protections, including overcurrent, overvoltage, and thermal safeguards, ensure safe operation and protect both the load and the DUT.
Each component contributes to the device’s functionality, making it an essential tool for testing and development.
Modes of Operation
A significant advantage of DC electronic loads lies in their ability to simulate various load conditions through different operational modes. These include:
1.Constant Current (CC) Mode
In this mode, the load maintains a fixed current regardless of the input voltage. It is commonly used to test batteries and power supplies for their stability and capacity.
Example: Testing a battery to determine how long it can deliver a specific current before discharging completely.
2.Constant Voltage (CV) Mode
The load maintains a constant voltage while drawing variable current. This is ideal for testing voltage regulation in power sources.
Example: Evaluating a solar panel’s voltage output under varying sunlight conditions.
3.Constant Resistance (CR) Mode
Here, the load mimics a fixed resistance, useful for evaluating resistive circuits or components.
Example: Testing heating elements or resistive loads in a circuit.
4.Constant Power (CP) Mode
The load adjusts its current dynamically to maintain a constant power draw, which is helpful for testing devices like DC-DC converters under real-world conditions.
Example: Simulating a laptop’s power consumption profile during use.
By understanding these modes, you can see how the flexibility of a DC electronic load answers the question of what is DC electronic load in practical scenarios.
Applications of DC Electronic Load
The versatility of DC electronic loads means they find applications in various industries and fields, including:
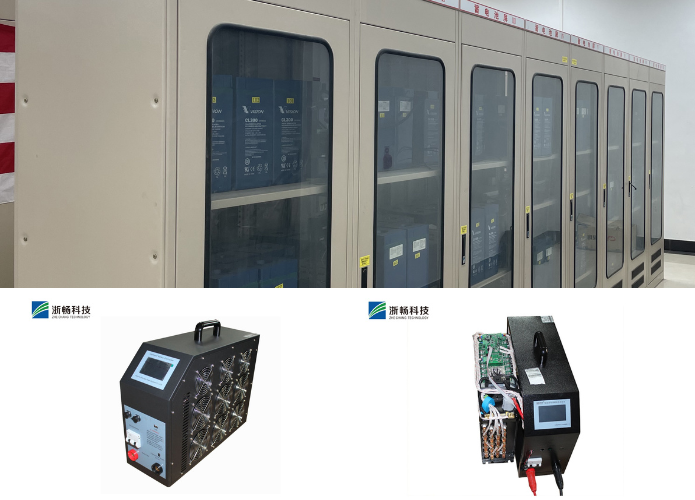
1.Battery Testing
Measuring capacity, charge/discharge cycles, and internal resistance.
Simulating real-world usage conditions for battery packs used in electric vehicles, smartphones, or renewable energy storage systems.
2.Power Supply Testing
Assessing the efficiency, stability, and thermal performance of power supplies under different loads.
Simulating short circuits and other adverse conditions to test protection mechanisms.
3.Solar Panel Testing
Evaluating the performance of solar cells under varying loads and conditions.
Measuring maximum power point tracking (MPPT) efficiency to ensure optimal energy conversion.
4.Electronic Circuit Testing
Simulating real-world electrical loads on circuit components to evaluate their behavior and durability.
Stress testing components to identify potential points of failure.
These examples illustrate why understanding what is DC electronic load is crucial for anyone involved in electronics design or quality assurance.

Advantages of DC Electronic Load
Here are some key benefits that highlight the importance of DC electronic loads:
Precision and Control
The ability to program exact load parameters ensures high accuracy in testing and measurements, enabling engineers to obtain reliable data.
Versatility
With multiple operational modes, DC electronic loads adapt to a wide range of testing requirements, making them suitable for diverse applications.
Real-Time Monitoring
Integrated displays and data logging features allow users to observe and analyze performance metrics instantly, streamlining the testing process.
Enhanced Safety
Built-in protection mechanisms, such as overcurrent and overvoltage protection, prevent damage to both the device under test and the load itself.
Efficiency
Compared to traditional resistive loads, DC electronic loads are more energy-efficient and compact, reducing both operational costs and space requirements.
How to Select a DC Electronic Load
Now that we’ve covered what is DC electronic load, let’s explore how to choose the right one for your needs. Consider the following factors:
Voltage and Current Ratings
Ensure the load can handle the maximum voltage and current of your device under test. Exceeding these ratings could damage the load or produce inaccurate results.
Power Dissipation Capacity
Select a load with sufficient power dissipation capabilities to avoid overheating during high-power tests. Devices with advanced cooling systems are ideal for prolonged use.
Operational Modes
Look for a load that offers the modes you require, such as CC, CV, CR, and CP, to match your specific testing scenarios.
Interface and Connectivity
Modern loads with USB, Ethernet, or GPIB interfaces enable remote control and automation, which is essential for complex testing setups.
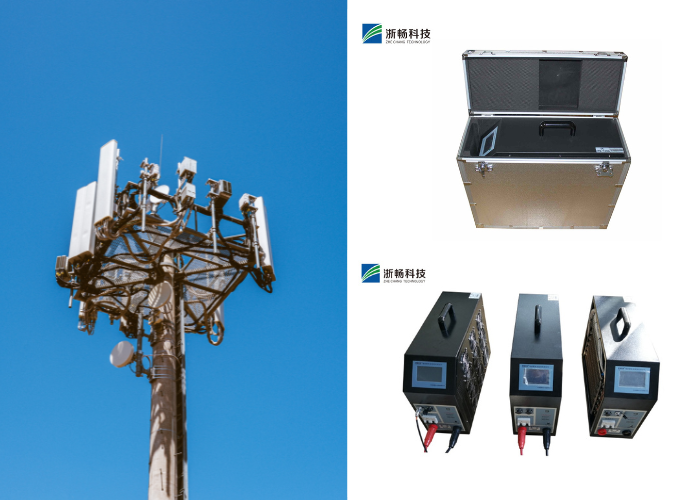
Portability and Size
For field testing, a compact and lightweight load is preferable, while laboratory settings may prioritize higher power ratings over portability.
Price and Warranty
Compare features, costs, and warranty terms to find the best value for your investment.
Conclusion
In summary, what is DC electronic load? It is an indispensable tool for anyone working in electronics testing, offering precision, versatility, and safety. From evaluating batteries and power supplies to testing solar panels and circuit components, DC electronic loads empower engineers to simulate real-world conditions and optimize their designs.
By understanding its components, modes of operation, and applications, you can unlock its full potential and ensure your testing processes are accurate and reliable. Whether you’re a professional engineer, technician, or electronics enthusiast, investing in the right DC electronic load can transform the way you approach testing and development.
Popular Battery Tester
Popular Battery Tester
Latest News
Latest News

Get Price of Battery Tester
Get Price of Battery Tester
Address:
Floor 3, Building 1, No.1418-60, Moganshan road, Hangzhou city, Zhejiang Province, China.310015

















































