What is a Battery Tester?
What are battery testers?
A battery tester is a device used to measure the state of charge, voltage, and overall health of a battery. It provides critical information about a battery's performance and condition, helping users determine if a battery is functioning properly or if it needs to be recharged or replaced. Battery testers come in various forms, including digital, analog, load testers, and conductance testers, each designed to perform specific types of assessments on different kinds of batteries.
Battery testers play a crucial role in maintaining the efficiency and reliability of batteries across various applications. They help prevent unexpected battery failures by identifying potential issues before they become serious problems. By regularly testing batteries, users can ensure they are always operating at optimal levels, thus extending the lifespan of the batteries and enhancing the safety of devices and systems that rely on them. In industries such as automotive, consumer electronics, renewable energy, and industrial applications, battery testers are essential tools for ensuring consistent and reliable power supply.
Types of Battery Testers
1. Digital Battery Testers
Digital battery testers are sophisticated devices equipped with LCD or LED displays that provide precise and clear readouts of a battery's condition. These testers can measure various parameters, including voltage, current, resistance, and overall battery health. Some advanced digital testers also come with additional functionalities such as data storage, which allows users to keep records of their battery tests, and Bluetooth connectivity for transferring data to other devices. They are often powered either by an internal battery or directly from the battery being tested.
The primary advantages of digital battery testers lie in their accuracy and ease of use. The digital readout eliminates the guesswork associated with interpreting needle positions on analog meters, making it easy for users to obtain precise measurements. Additionally, the portability and lightweight design of many digital testers make them convenient tools for a wide range of applications, from automotive diagnostics to home electronics maintenance. However, digital testers tend to be more expensive than their analog counterparts, and they require a power source, which could be a limitation in certain situations. Additionally, their complexity might pose a challenge for users who are not tech-savvy.
2. Analog Battery Testers
Analog battery testers, characterized by their needle-based gauge displays, offer a straightforward and reliable method for checking battery health. These testers are simple in design, typically featuring a dial or meter with a needle that moves to indicate the battery's charge level. One of the main benefits of analog testers is that they usually do not require an internal power source, making them always ready to use without worrying about battery life.
The simplicity of analog battery testers is both a strength and a limitation. They are generally more affordable and easier to use, making them accessible to a broader audience, including those who may not be comfortable with digital interfaces. However, analog testers are less precise than digital ones, and interpreting the needle's position can sometimes be challenging, especially for users with less experience. The lack of additional features, such as data storage or connectivity, also limits their functionality to basic testing needs.
3. Load Testers
Load testers work by applying a load to the battery, simulating real-world conditions to assess its performance. This method involves drawing a significant current from the battery for a short period, then measuring how well the battery maintains its voltage under this load. By doing so, load testers can provide a more accurate picture of the battery's true capacity and ability to perform under stress.
These testers are particularly suitable for automotive batteries and other high-capacity batteries used in industrial applications. They are highly effective in diagnosing issues with lead-acid and deep-cycle batteries, which are commonly used in cars, trucks, and heavy machinery. Load testers can identify problems that other types of testers might miss, such as a battery's inability to deliver adequate power under load, which is crucial for applications where reliable performance is essential. However, they are generally larger and more cumbersome than other types of testers, and they can be more expensive and complex to operate.
4. Conductance Testers
Conductance testers measure a battery's conductance, which is the inverse of its resistance. This method involves sending a small, alternating current through the battery and measuring the voltage response. The resulting conductance value provides an indication of the battery's ability to conduct electrical current, which correlates with its overall health and capacity.
These testers are widely used in the automotive industry for testing car batteries, where quick and accurate assessments are necessary. Conductance testing is non-invasive and can be performed rapidly, making it suitable for routine maintenance checks in large battery banks, such as those used in telecommunications or uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems. The main advantage of conductance testers is their speed and accuracy, allowing for frequent monitoring without significant downtime. However, while they are excellent for identifying failing batteries, they might not provide as detailed an analysis of a battery's condition under actual operating conditions as load testers do.
Components of a Battery Tester
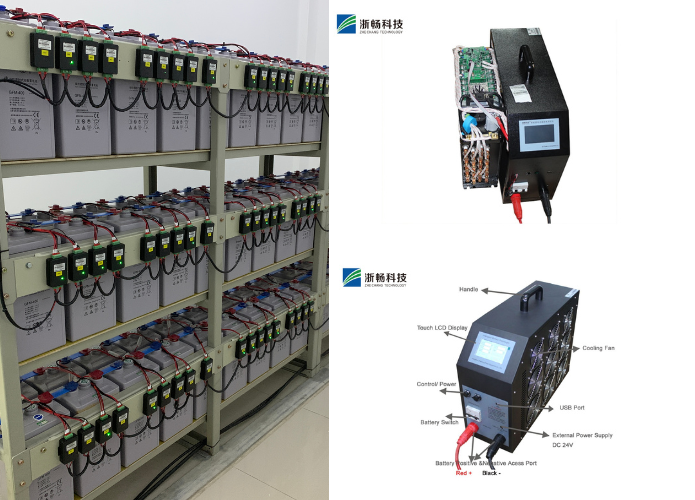
1. Display Screen
The display screen is one of the most critical components of a battery tester, serving as the primary interface between the device and the user. In digital battery testers, the display screen is typically an LCD or LED panel that provides clear and precise readouts of the battery's condition, including voltage, current, resistance, and overall health status. The clarity and accuracy of the display screen allow users to quickly interpret the results without any guesswork. Some advanced models may also feature backlit displays for easy reading in low-light conditions and additional functions such as graphical displays or multi-line readouts for more detailed information.
2. Probes or Clamps
Probes or clamps are the components that make direct contact with the battery terminals to conduct measurements. These are usually insulated to ensure user safety and are designed to provide a secure and stable connection to the battery. Probes are commonly used for small batteries and precision testing, while clamps are more suitable for larger batteries, such as those found in automobiles, due to their robust and secure grip. High-quality probes and clamps ensure accurate readings by minimizing resistance at the contact points and preventing slippage or poor connections during testing.
3. Internal Circuitry
The internal circuitry of a battery tester is the backbone of the device, responsible for processing the measurements taken from the battery. This circuitry includes various electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, and microcontrollers that work together to measure voltage, current, and resistance accurately. In digital testers, the circuitry also converts analog signals into digital data, which is then displayed on the screen. The precision and reliability of the internal circuitry are crucial for providing accurate and consistent test results, and high-quality circuitry can differentiate a superior tester from a mediocre one.
4. Power Source for the Tester
The power source for the battery tester is another essential component, especially for digital testers that require electricity to operate their displays and internal circuitry. Many digital testers are powered by small internal batteries, such as AA or AAA cells, or rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. Some models may draw power directly from the battery being tested, which can be convenient but may also affect the battery's state during the test. Analog testers, on the other hand, typically do not require an external power source, relying instead on the battery's own power for their operation. Ensuring that the power source is reliable and easily replaceable or rechargeable is important for the tester's longevity and usability.
Together, these components—display screen, probes or clamps, internal circuitry, and power source—form the core of a battery tester, each playing a vital role in ensuring accurate, reliable, and user-friendly battery assessments.
How Battery Testers Work
1. Measuring Voltage
Measuring voltage is one of the primary functions of a battery tester. Voltage measurement provides an immediate indication of the battery's state of charge. When a battery tester is connected to a battery, it measures the potential difference between the positive and negative terminals. This measurement is displayed in volts (V) and gives users a quick snapshot of how much charge the battery holds. For instance, a fully charged lead-acid car battery should typically read around 12.6 volts, while a reading below 12 volts suggests the battery may be discharged or failing. Accurate voltage measurement is essential for diagnosing battery health and ensuring it can deliver the required power to devices or vehicles.
2. Assessing Internal Resistance
Internal resistance is a key parameter in determining a battery's health and efficiency. High internal resistance indicates that a battery is deteriorating and may not perform well under load. Battery testers assess internal resistance by passing a small, known current through the battery and measuring the resulting voltage drop. This measurement helps to calculate the resistance using Ohm's law (R = V/I). A low internal resistance means the battery can efficiently deliver current to a load, while high resistance can cause voltage drops and overheating, leading to poor performance. Regularly assessing internal resistance helps identify aging batteries that might still hold a charge but are unable to deliver power effectively.
3. Testing Load Capacity
Testing load capacity involves evaluating how a battery performs under real-world conditions. Load testers apply a significant current load to the battery for a short period, simulating the demands that will be placed on the battery during actual use. By monitoring how well the battery maintains its voltage under this load, testers can determine its true capacity and performance. A battery that can maintain a stable voltage under load is considered healthy, while a significant voltage drop indicates that the battery might struggle to power devices or vehicles reliably. This type of testing is particularly important for automotive batteries, where reliable performance under high load conditions is critical.
4. Interpreting Results
Interpreting the results from a battery tester involves understanding the measurements and determining the battery's condition. For voltage readings, specific thresholds indicate whether a battery is fully charged, partially charged, or discharged. Internal resistance values help diagnose the battery's efficiency and potential issues like sulfation in lead-acid batteries. Load testing results provide insights into the battery's ability to perform under stress. Modern digital testers often provide clear indications or diagnostic messages, such as "Good," "Replace," or "Recharge," making it easier for users to make decisions. Accurate interpretation of these results is essential for maintaining battery health, ensuring safety, and avoiding unexpected failures.

Applications of Battery Testers
1. Automotive Industry
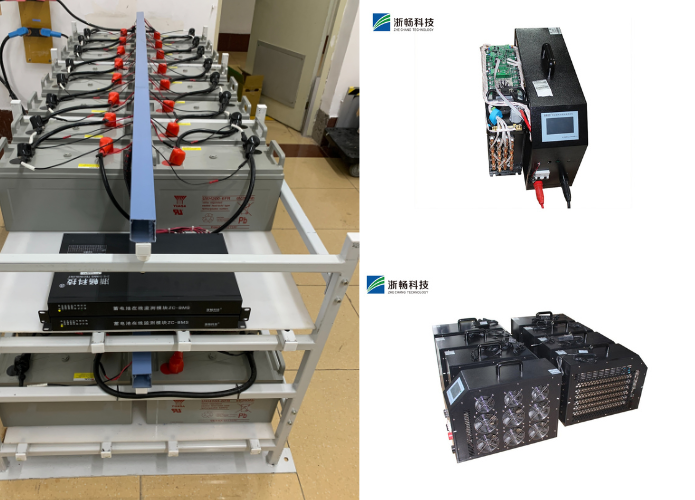
In the automotive industry, battery testers are essential tools for ensuring the reliability and performance of vehicle batteries. Automotive batteries must provide a consistent and powerful current to start engines, operate lights, and power various electronic systems. Regular testing of these batteries can prevent unexpected breakdowns by identifying weak or failing batteries before they completely fail. Mechanics and technicians use battery testers to check the state of charge, internal resistance, and load capacity of car batteries, providing insights into whether a battery needs to be recharged, serviced, or replaced. Additionally, for hybrid and electric vehicles, battery testers help monitor the health of high-voltage battery packs, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
2. Consumer Electronics
Battery testers play a crucial role in the maintenance and longevity of consumer electronics. Devices such as smartphones, laptops, tablets, and cameras rely on rechargeable batteries for their operation. Regular testing of these batteries ensures they are functioning correctly and holding a proper charge. Battery testers help users and technicians determine when a battery has degraded to the point where it needs to be replaced, thus avoiding sudden device shutdowns and extending the overall lifespan of the electronics. With the proliferation of portable devices, the demand for reliable battery performance has made battery testers indispensable in consumer electronics maintenance.
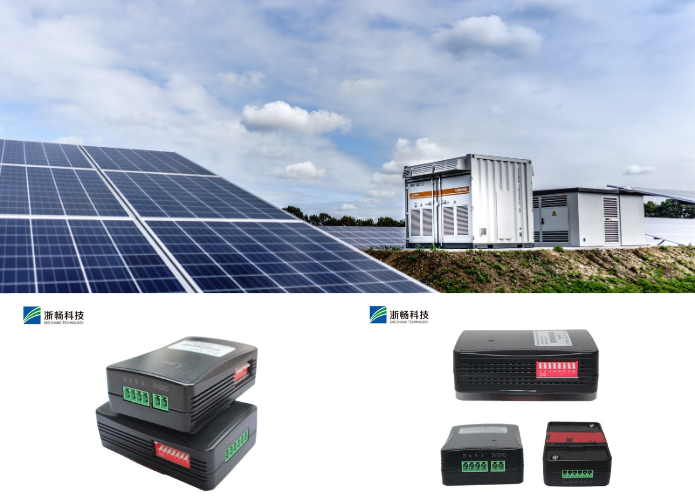
3. Renewable Energy Systems
In renewable energy systems, such as solar and wind power installations, battery storage is critical for managing energy supply and demand. Battery testers are vital in these systems to ensure the health and efficiency of energy storage batteries, which are often large and expensive. These batteries need to store energy generated during peak production times and release it during periods of low production or high demand. Regular testing helps maintain the batteries' performance, ensures the reliability of the energy supply, and extends the lifespan of the storage systems. Accurate battery testing in renewable energy applications supports sustainable energy management and helps in achieving energy independence goals.
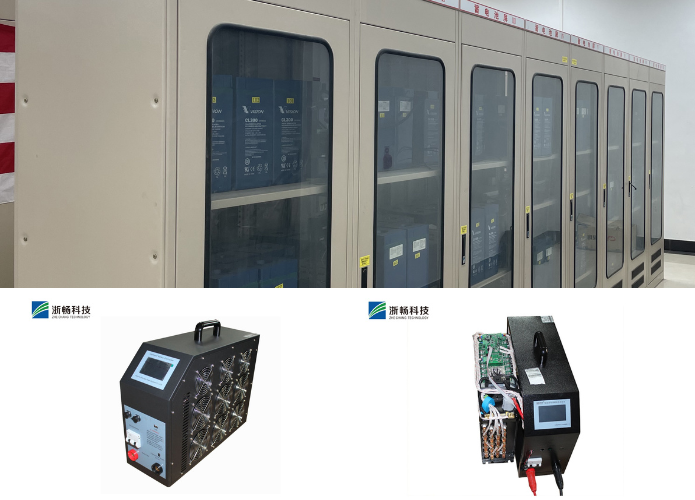
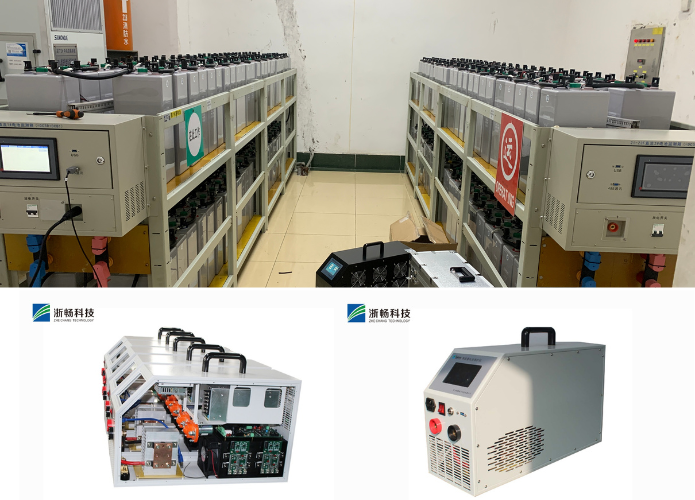
4. Industrial Applications
In industrial applications, battery testers are used to maintain the reliability of backup power systems, machinery, and equipment that rely on batteries for operation. Industries such as manufacturing, telecommunications, and data centers depend on uninterrupted power supplies (UPS) and backup batteries to prevent costly downtime and data loss. Battery testers help in monitoring and maintaining these backup systems by providing accurate assessments of battery health, charge levels, and load capacities. This ensures that batteries are always ready to perform in critical situations, reducing the risk of unexpected failures and enhancing the overall efficiency and safety of industrial operations.
In each of these applications, battery testers provide invaluable insights into the performance and condition of batteries, helping to prevent failures, extend battery life, and ensure reliable operation across a wide range of devices and systems.
Benefits of Using Battery Testers
1. Ensuring Battery Health and Longevity
Battery testers play a crucial role in maintaining the health and extending the lifespan of batteries. By regularly monitoring a battery's condition, these testers provide detailed insights into its performance and potential issues. Early detection of problems such as reduced capacity, internal resistance, and other anomalies allows for timely maintenance and replacement. This proactive approach helps in avoiding the premature failure of batteries, ensuring that they last longer and perform optimally throughout their intended lifespan. Regular testing also aids in maintaining the manufacturer's recommended maintenance schedules, further promoting battery longevity.
2. Preventing Unexpected Failures
One of the primary benefits of using battery testers is the prevention of unexpected battery failures. In critical applications, such as in medical devices, emergency systems, and industrial machinery, a sudden battery failure can lead to significant disruptions and potentially hazardous situations. Battery testers help in identifying weak or failing batteries before they completely fail, allowing for scheduled replacements or repairs. This foresight minimizes downtime, enhances the reliability of battery-dependent systems, and ensures continuity in operations. By avoiding unexpected failures, businesses can save on emergency repair costs and protect their valuable equipment.
3. Enhancing Safety
Battery testers contribute significantly to enhancing safety in various applications. Batteries, especially those used in high-power applications, can pose safety risks if they are not in good condition. Issues like overcharging, overheating, and leakage can lead to dangerous situations such as fires or explosions. Regular testing ensures that batteries are operating within safe parameters, reducing the risk of such hazardous events. Additionally, battery testers can identify potential safety concerns early, allowing for preventative measures to be taken before they escalate into serious problems. This proactive safety management is essential in environments where battery safety is critical, such as in electric vehicles and aerospace.
4. Optimizing Performance
Optimizing the performance of batteries is another significant advantage of using battery testers. Performance optimization involves ensuring that batteries are functioning at their best capacity and efficiency. Through regular testing, users can fine-tune charging and discharging cycles, balance cell performance, and identify the best usage patterns to maximize battery efficiency. This is particularly important in applications where battery performance directly impacts operational efficiency, such as in renewable energy systems, electric vehicles, and portable electronic devices. By maintaining batteries at peak performance, battery testers help in achieving better energy management, reducing operational costs, and enhancing the overall user experience.
How to Use a Battery Tester
1. Safety Precautions
Before using a battery tester, it is essential to observe several safety precautions to ensure a safe and accurate testing process:
* Wear Protective Gear: Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves and safety goggles to protect against accidental spills or short circuits.
* Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: Ensure you are in a well-ventilated area to avoid the buildup of harmful gases that some batteries may emit.
* Check for Damage: Inspect the battery and tester for any visible damage or leaks before starting. Do not test a visibly damaged or leaking battery.
* Read the Manual: Review the battery tester’s manual for specific instructions and safety guidelines relevant to the device you are using.
* Avoid Metal Jewelry: Remove any metal jewelry or conductive materials that could cause short circuits during the testing process.
* Power Off Equipment: Ensure that the battery is disconnected from any equipment and power is turned off before testing.
2. Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Identify the Battery Type: Determine the type of battery you are testing (e.g., lead-acid, lithium-ion, NiMH) and set the tester accordingly if it has multiple settings.
Step 2: Connect the Probes: Attach the battery tester’s probes to the battery terminals. Typically, the red probe connects to the positive terminal and the black probe to the negative terminal.
Step 3: Turn On the Tester: Power on the battery tester. Some testers will automatically start the testing process, while others may require you to select a specific test type or mode.
Step 4: Select the Test Mode: Choose the appropriate test mode based on what you are evaluating (e.g., voltage, current, internal resistance).
Step 5: Initiate the Test: Start the test by pressing the relevant button or setting on the tester. Ensure that the probes remain securely connected during the test.
Step 6: Wait for Results: Allow the tester to complete the evaluation. This may take a few seconds to several minutes depending on the type of test.
Step 7: Record the Readings: Once the test is complete, note the readings displayed on the tester. Some testers may have a hold function to freeze the readout for easier recording.
3. Interpreting the Readouts
Interpreting the readouts from a battery tester is crucial for understanding the battery’s condition:
* Voltage: This is the most common readout. A fully charged battery should show a voltage close to its rated value (e.g., 12.6V for a fully charged 12V lead-acid battery). A significantly lower voltage indicates that the battery may be discharged or failing.
* Current (Amperage): Some testers measure the current output under load. A battery should provide a current close to its rated capacity. Lower than expected current indicates potential issues.
* Internal Resistance: This readout indicates the battery’s internal resistance. Higher resistance suggests aging or failing cells, which can lead to reduced performance.
* State of Charge (SoC): Many modern testers provide a direct SoC percentage. This indicates how much charge remains in the battery.
* State of Health (SoH): Advanced testers offer an SoH percentage, reflecting the overall health and remaining lifespan of the battery.
* Error Codes or Messages: Some testers may display specific error codes or messages if the battery is faulty or the test could not be completed.
Maintenance and Care of Battery Testers
1. Proper Storage
Proper storage of battery testers is essential to maintain their accuracy and longevity:
* Store in a Cool, Dry Place: Keep the battery tester in an environment that is cool, dry, and free from excessive humidity or temperature fluctuations. Extreme conditions can damage the internal components.
* Avoid Direct Sunlight: Store the tester away from direct sunlight to prevent overheating and potential damage to the casing and electronic components.
* Use a Protective Case: If possible, store the tester in a protective case to shield it from dust, moisture, and mechanical shocks.
* Disconnect Probes: When not in use, disconnect the probes from the tester and store them properly to prevent bending or damage to the connectors.
* Battery Storage: If the tester uses removable batteries, ensure they are stored separately and removed if the tester will not be used for an extended period. This prevents battery leakage and corrosion.
2. Regular Calibration
Regular calibration is crucial to ensure the accuracy of battery testers:
* Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Adhere to the calibration schedule recommended by the manufacturer, typically outlined in the user manual.
* Use Calibration Standards: Utilize appropriate calibration standards or reference materials to calibrate the tester. These standards should be traceable to national or international standards to ensure accuracy.
* Professional Calibration Services: For high-precision testers, consider using professional calibration services that can provide certified calibration and traceability documentation.
* Record Keeping: Maintain a calibration log that documents the dates of calibration, the standards used, and any adjustments made. This helps in tracking the tester’s performance over time.
* Check After Heavy Use: After periods of heavy use or exposure to extreme conditions, check and calibrate the tester to ensure it remains accurate.
3. Handling and Cleaning
Proper handling and cleaning of battery testers extend their operational life and maintain performance:
* Handle with Care: Always handle the tester gently, avoiding drops or impacts that could damage internal components.
* Clean Probes Regularly: Clean the probes using a soft cloth or a cleaning solution recommended by the manufacturer. Dirty or corroded probes can lead to inaccurate readings.
* Avoid Harsh Chemicals: Use mild cleaning solutions and avoid harsh chemicals that can damage the tester’s casing or internal circuits.
* Inspect Cables and Connectors: Regularly inspect cables and connectors for signs of wear, fraying, or damage. Replace any damaged components to ensure accurate measurements and safety.
* Wipe Down the Device: Periodically wipe down the tester’s exterior with a soft, damp cloth to remove dust and debris. Ensure the device is powered off and disconnected from any power sources during cleaning.
* Store Properly After Use: After each use, store the tester and its accessories properly to prevent damage and ensure they are ready for the next testing session.

Conclusion
Battery testers are invaluable tools for ensuring the health, longevity, and performance of batteries across a wide range of applications. By regularly monitoring battery condition, testers help in early detection of potential issues, preventing unexpected failures, and optimizing battery performance. They enhance safety by identifying and mitigating risks associated with battery malfunctions, such as overheating or leakage. The ability to interpret detailed readouts enables users to make informed decisions regarding battery maintenance and replacement, ultimately leading to cost savings and increased operational efficiency.
Selecting the right battery tester involves considering factors such as the types of batteries you use, the specific parameters you need to measure, and the level of accuracy required. High-quality testers with advanced features like internal resistance measurement, state of charge (SoC), and state of health (SoH) indicators provide more comprehensive insights into battery condition.
Using battery testers effectively requires adherence to safety precautions, following a systematic testing process, and correctly interpreting the results. Regular maintenance, including proper storage, calibration, and careful handling, ensures that the tester remains reliable and accurate over time. By integrating battery testers into your routine maintenance protocols, you can significantly enhance the reliability and efficiency of your battery-dependent systems, ensuring uninterrupted and safe operations.
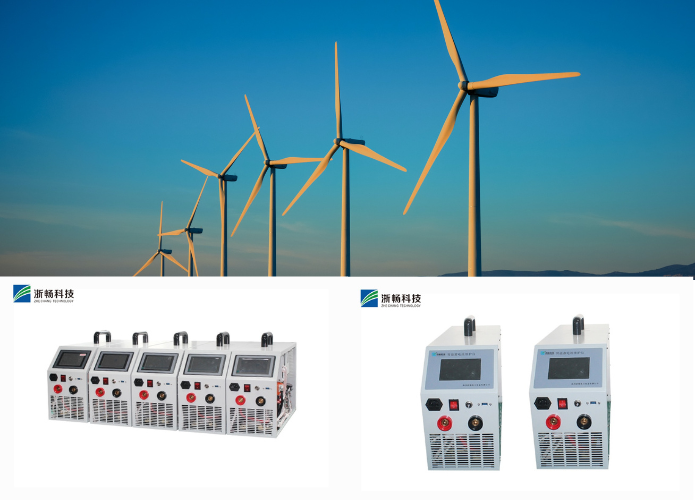
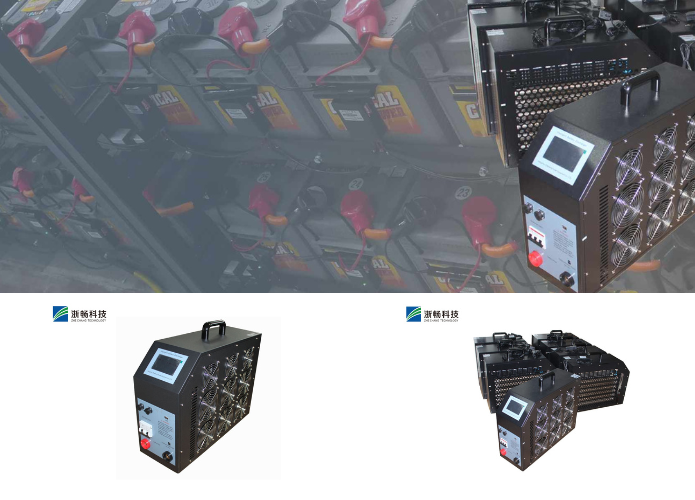
Zhechang Battery Testers
Zhechang is a leading manufacturer of high-quality battery testers designed to meet the diverse needs of various industries. Their battery testers are known for their precision, reliability, and advanced features, making them suitable for both professional and personal use. Whether you are maintaining automotive batteries, industrial power systems, or consumer electronics, Zhechang offers a range of testers that cater to different battery types and testing requirements.
Key Features and Advantages
* Advanced Testing Capabilities: Zhechang battery testers are equipped with advanced functions such as internal resistance measurement, state of charge (SoC) and state of health (SoH) indicators, and detailed voltage and current analysis. These features provide comprehensive insights into battery condition and performance.
* User-Friendly Interface: The testers feature intuitive interfaces with clear displays and easy-to-navigate menus, ensuring that users can quickly and accurately perform tests and interpret the results.
* Robust Design: Built to withstand demanding environments, Zhechang battery testers are durable and reliable. They are designed with rugged casings and high-quality components to ensure long-term use in various settings.
* Wide Compatibility: Zhechang offers testers compatible with a wide range of battery types, including lead-acid, lithium-ion, nickel-metal hydride (NiMH), and more. This versatility makes them suitable for numerous applications, from automotive maintenance to industrial power management.
* Accurate Calibration: Each tester is calibrated to precise standards, ensuring that measurements are accurate and reliable. Regular calibration services are also available to maintain the tester's performance over time.
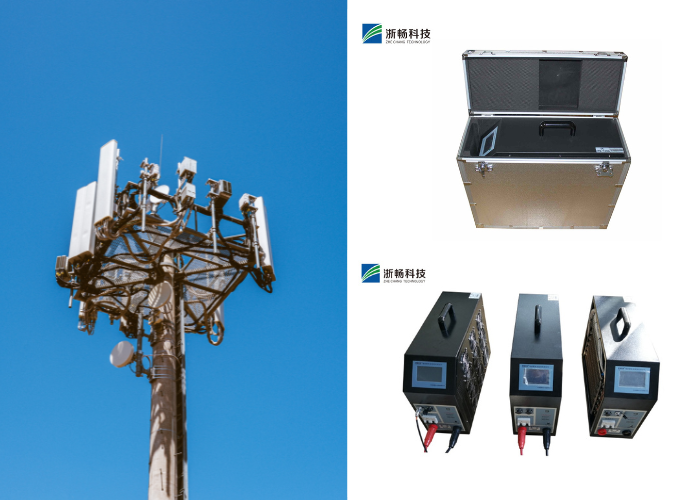
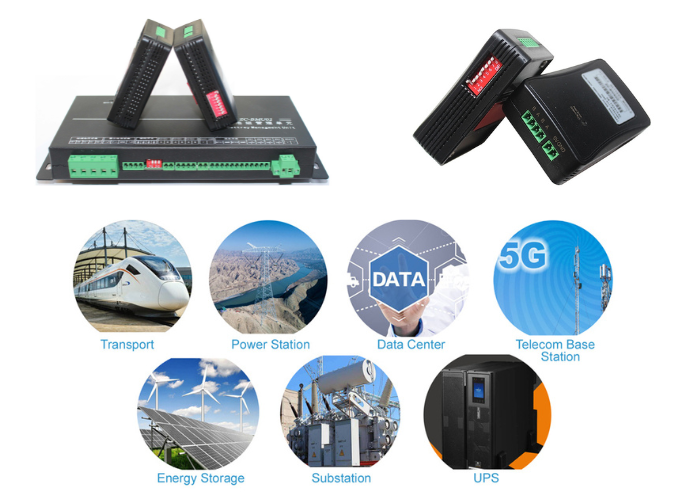
Applications of Zhechang Battery Testers
* Automotive Industry: Zhechang battery testers are widely used in the automotive industry for testing car batteries, ensuring they are in good condition and preventing unexpected breakdowns.
* Renewable Energy Systems: In solar and wind energy systems, these testers help maintain the efficiency and reliability of battery storage units, ensuring optimal performance.
* Industrial Maintenance: For industrial applications, Zhechang testers provide essential data for maintaining large-scale battery banks and backup power systems, preventing costly downtime.
* Consumer Electronics: Technicians use these testers to check the health and performance of batteries in consumer electronics, from smartphones to laptops, ensuring user safety and device longevity.
Choosing the Zhechang battery tester, whether it's a battery voltage tester, battery capacity meter, or battery analyser, depends on your specific needs and the types of batteries you work with. Consider the features that are most important for your applications, such as the ability to measure internal resistance, provide detailed readouts, and offer compatibility with different battery types.
To use Zhechang battery testers effectively, always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and safety precautions. Regularly calibrate your tester, whether it’s a battery voltage tester, battery capacity meter, or battery analyser, to maintain accuracy. Handle it with care to extend its lifespan. By integrating Zhechang battery testers into your maintenance routine, you can ensure that your batteries remain in optimal condition, thereby enhancing the efficiency and reliability of your battery-powered systems and devices.
In conclusion, Zhechang battery testers, including their battery voltage testers, battery capacity meters, and battery analysers, are a valuable investment for anyone involved in battery maintenance and management. Their advanced features, robust design, and wide compatibility make them a trusted choice for professionals and hobbyists alike, ensuring that batteries perform at their best and last longer.
Popular Battery Tester
Popular Battery Tester
Latest News
Latest News


Get Price of Battery Tester
Get Price of Battery Tester
Address:
Floor 3, Building 1, No.1418-60, Moganshan road, Hangzhou city, Zhejiang Province, China.310015