The Importance of Battery Internal Resistance Test in Performance Evaluation
In today’s technology-driven world, batteries are essential components powering a myriad of devices, from smartphones and laptops to electric vehicles and renewable energy systems. Understanding the performance and longevity of these batteries is crucial, and one of the most effective ways to assess battery health is through the battery internal resistance test. This blog explores the significance of internal resistance testing, how it is conducted, and its implications for various battery applications, including a specific focus on the 12V battery internal resistance test.
What is Internal Resistance?
Internal resistance is the opposition within a battery to the flow of electric current. It can significantly influence a battery's performance, affecting how efficiently it delivers power and how long it lasts under load. Internal resistance consists of several components, including:
Electrolytic resistance: Caused by the electrolyte’s conductivity.
Electrode resistance: Arising from the materials and construction of the electrodes.
Connection resistance: Resulting from the connections within the battery system.
As batteries age or undergo cycles of charging and discharging, their internal resistance tends to increase. This rise can lead to reduced efficiency and capacity, making it crucial to monitor and evaluate internal resistance regularly.

Why is Battery Internal Resistance Testing Important?
1. Performance Evaluation
The battery internal resistance test provides insights into the performance of a battery. Higher internal resistance can indicate that a battery is struggling to deliver the necessary current, which may lead to reduced efficiency and power output. Regular testing helps identify batteries that are underperforming, allowing for timely interventions or replacements.
2. State of Health Assessment
Internal resistance is a key indicator of a battery's state of health (SoH). A significant increase in internal resistance can signal that a battery is deteriorating, potentially failing or reaching the end of its life cycle. By performing an internal resistance test, users can gauge the overall condition of the battery and make informed decisions about its usage, maintenance, or replacement.
3. Predictive Maintenance
For organizations relying on batteries for critical applications—such as backup power systems, electric vehicles, or renewable energy systems—predictive maintenance is vital. Conducting regular 12V battery internal resistance tests allows operators to predict failures before they occur, minimizing downtime and ensuring operational efficiency. By identifying batteries that exhibit abnormal internal resistance, maintenance can be scheduled proactively, avoiding unexpected failures and associated costs.
4. Battery Management System Optimization
Battery management systems (BMS) play a crucial role in managing battery performance and health. By incorporating internal resistance data into the BMS algorithms, operators can optimize charging and discharging cycles, enhance battery life, and improve overall system efficiency. A comprehensive understanding of a battery's internal resistance enables better decision-making in energy management and resource allocation.
How to Conduct a Battery Internal Resistance Test
Conducting a battery internal resistance test is a straightforward process that can be performed using various methods, including specialized battery testers and multimeters. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to carry out the test:
Step 1: Gather Equipment
To perform the internal resistance test, you will need:
A battery tester with internal resistance measurement capability or a high-quality multimeter.
Safety equipment, such as gloves and goggles.
A fully charged battery for accurate measurements.
Step 2: Prepare the Battery
Ensure the battery is fully charged before testing. Disconnect any loads or devices connected to the battery to avoid interference with the test results. If testing a 12V battery, confirm that it is in good condition and clean the terminals to ensure good contact.
Step 3: Connect the Tester
1.For a Dedicated Battery Tester:
Connect the tester’s positive lead to the battery's positive terminal and the negative lead to the negative terminal.
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to initiate the internal resistance test.
2.For a Multimeter:
Set the multimeter to measure resistance (Ohms).
Connect the multimeter leads to the respective battery terminals (positive to positive, negative to negative).
Step 4: Perform the Test
Activate the tester or multimeter to measure the internal resistance. Depending on the device used, you may receive a direct reading of the internal resistance in Ohms. If using a multimeter, ensure the readings stabilize before recording the value.
Step 5: Analyze the Results
Compare the measured internal resistance against manufacturer specifications or established benchmarks. Higher-than-expected resistance values indicate potential issues with the battery, such as sulfation or electrolyte degradation. Regular testing can reveal trends over time, helping to predict when a battery may need replacement.
Factors Influencing Battery Internal Resistance
Several factors can influence the internal resistance of a battery, impacting its performance and longevity. Understanding these factors can help users make informed decisions regarding maintenance and usage.
1. Temperature
Temperature has a significant impact on internal resistance. Higher temperatures can lower internal resistance, improving battery performance. Conversely, colder temperatures can increase resistance, leading to reduced efficiency and capacity. It’s essential to consider the operating temperature range of batteries and conduct internal resistance tests accordingly.
2. State of Charge
The state of charge (SoC) of a battery can also affect internal resistance. A fully charged battery typically exhibits lower internal resistance compared to a partially charged or depleted battery. Performing an internal resistance test at different states of charge can provide valuable insights into a battery's health.
3. Battery Chemistry
Different battery chemistries exhibit varying internal resistance characteristics. For example, lithium-ion batteries tend to have lower internal resistance than lead-acid batteries. Understanding the specific chemistry of a battery can help in interpreting internal resistance test results.
4. Cycle Life and Aging
As batteries undergo charging and discharging cycles, their internal resistance typically increases. Aging effects, such as electrode degradation and electrolyte depletion, contribute to this phenomenon. Regular testing helps monitor these changes over time, allowing for proactive management.
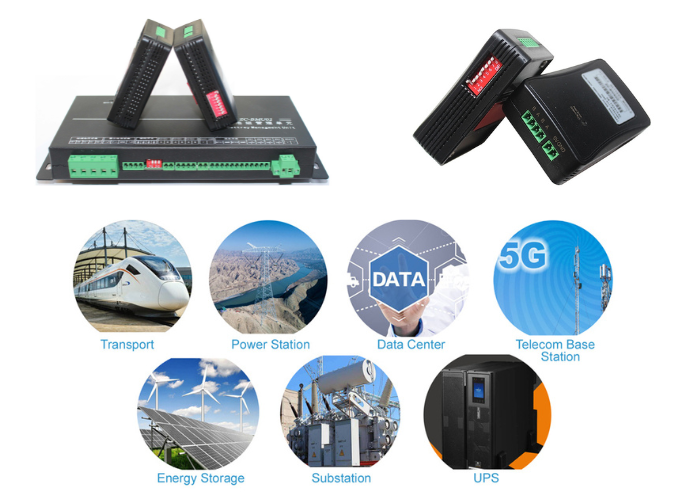
Applications of Battery Internal Resistance Testing
Battery internal resistance testing is crucial across various applications, providing insights that enhance performance and reliability.
1. Electric Vehicles (EVs)
In electric vehicles, the performance of battery packs is paramount. Conducting 12V battery internal resistance tests enables manufacturers and operators to ensure that battery packs are functioning optimally, leading to improved range and performance. Monitoring internal resistance can also help identify failing cells within battery packs, facilitating timely replacements.
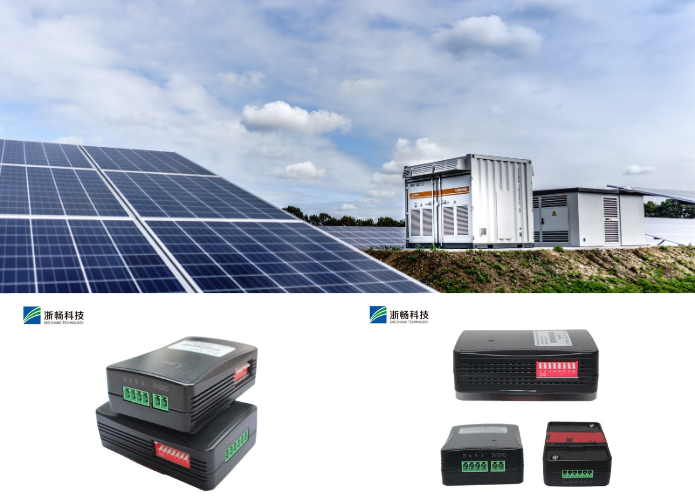
2. Renewable Energy Systems
In renewable energy systems, such as solar or wind power storage, battery performance directly impacts energy availability. Regular internal resistance testing ensures that batteries are performing efficiently, maximizing the return on investment for renewable energy installations.
3. Backup Power Systems
For critical applications, such as uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) or backup generators, ensuring battery reliability is essential. Conducting internal resistance tests regularly helps maintain battery health, reducing the risk of failure during power outages.
4. Consumer Electronics
In consumer electronics, such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops, understanding battery health is vital for user satisfaction. Manufacturers can use internal resistance testing to optimize battery performance, enhance longevity, and provide better warranties.

Conclusion
The battery internal resistance test is a powerful tool in performance evaluation, offering valuable insights into the health and efficiency of batteries across various applications. By understanding the significance of internal resistance, users can make informed decisions about maintenance, replacement, and performance optimization.
Regular testing not only enhances battery performance but also contributes to predictive maintenance strategies, ensuring reliability in critical applications. As battery technology continues to evolve, the importance of internal resistance testing will only increase, underscoring the need for robust monitoring practices in all battery-powered systems.
Incorporating routine internal resistance tests, especially for common battery types like the 12V battery, will help users maximize performance, extend battery life, and prevent unexpected failures. As we continue to rely on batteries in our daily lives, understanding and optimizing their performance through internal resistance testing will be crucial for future advancements in technology and energy management.
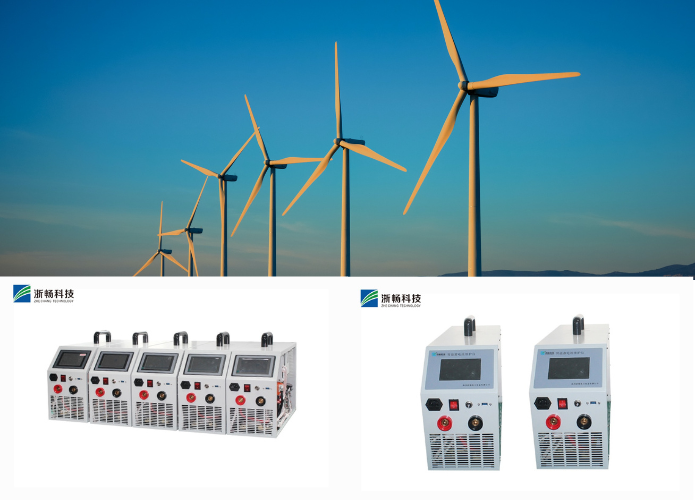
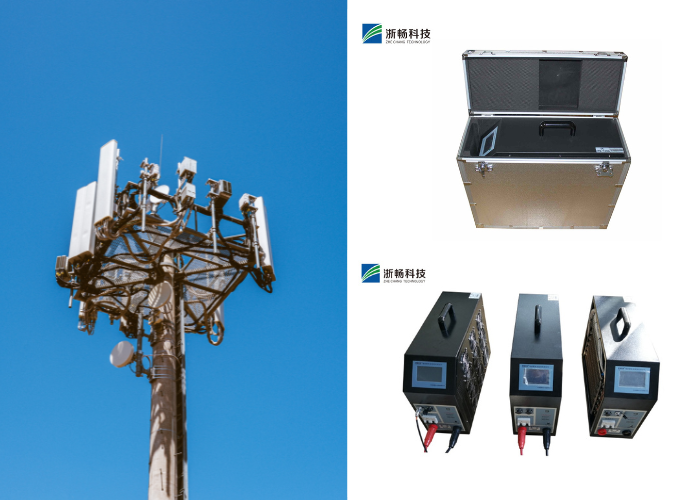
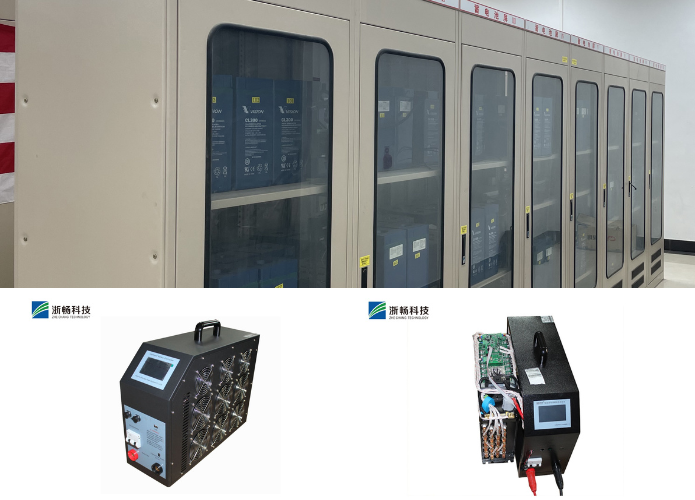
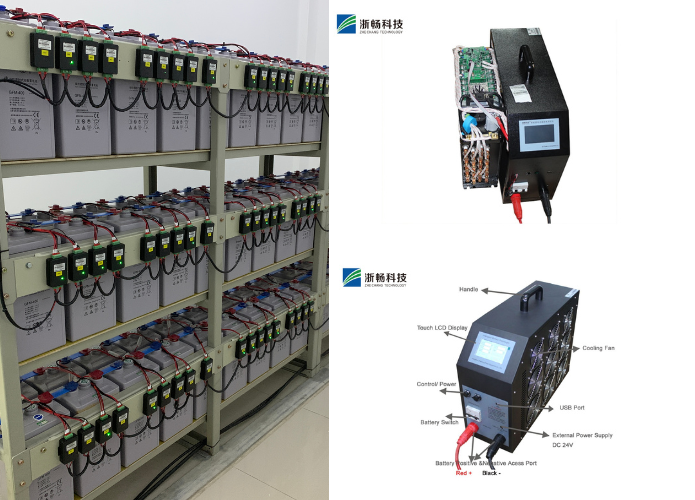
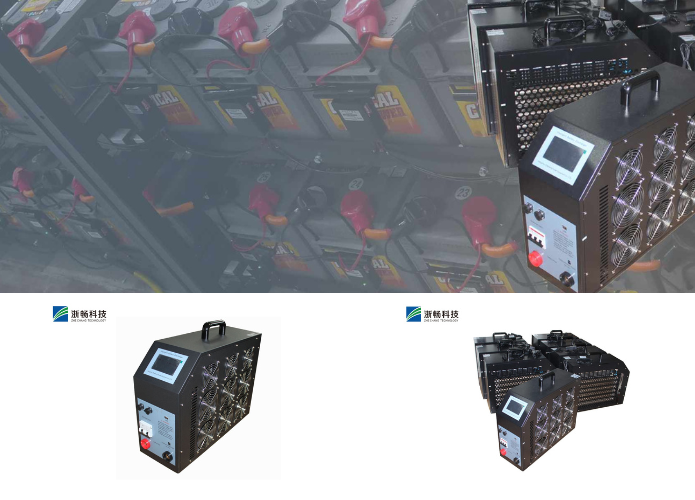
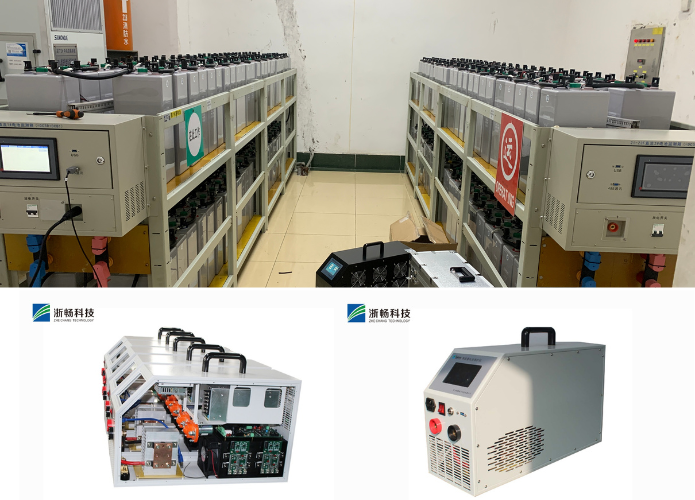
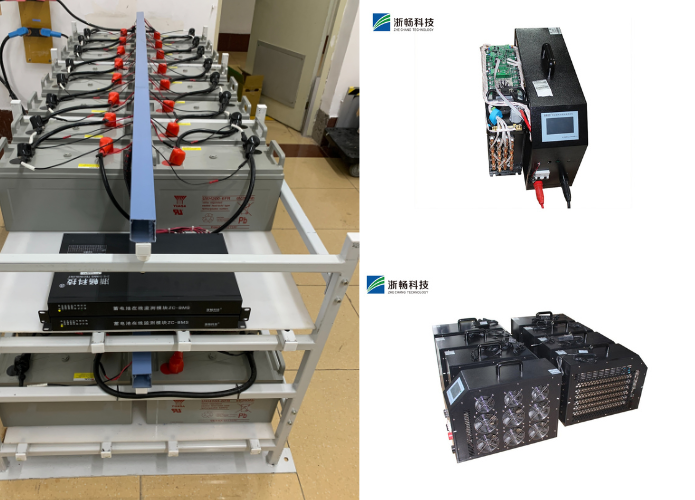
Popular Battery Tester
Popular Battery Tester
Latest News
Latest News


Get Price of Battery Tester
Get Price of Battery Tester
Address:
Floor 3, Building 1, No.1418-60, Moganshan road, Hangzhou city, Zhejiang Province, China.310015