How to Measure Internal Resistance Battery
The internal resistance of a battery is a critical parameter that significantly impacts its performance, efficiency, and lifespan. Whether you're working with automotive batteries, lithium-ion cells, or other types, understanding how to measure internal resistance battery is essential for assessing its health and suitability for specific applications. In this guide, we’ll delve deep into the topic, covering the basics, methods, tools, and applications related to this vital measurement.
What is Internal Resistance in a Battery?
Internal resistance is the opposition a battery offers to the flow of electric current within its structure. It arises due to the inherent material properties, design, and chemical processes inside the battery. This resistance directly affects the battery’s ability to deliver power, its efficiency, and its temperature under load.
Key Factors Influencing Internal Resistance:
- Material Quality: The materials used in a battery’s electrodes and electrolyte can influence the internal resistance. For instance, a battery made with high-purity materials tends to have lower internal resistance compared to one made with lower-quality materials.
- Battery Design: The design and configuration of a battery play a significant role in internal resistance. For example, a battery with a larger surface area for electrodes typically has lower internal resistance because the current can flow more freely.
- Age and Usage: As a battery ages, its internal resistance increases. This is because of chemical changes, like the buildup of resistive layers on the electrodes, and mechanical changes, such as electrode degradation. Additionally, the more a battery is used, the more wear and tear it experiences, which also leads to higher internal resistance.
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures can affect the internal resistance. For example, a battery might show a higher internal resistance at lower temperatures because the electrolyte becomes more viscous, making it harder for ions to flow. On the other hand, excessive heat can also cause internal resistance to increase, potentially leading to battery damage or failure.
Understanding how to measure internal resistance battery accurately is crucial to identifying these factors and their impact.

Why is Measuring Internal Resistance Important?
Measuring internal resistance provides insights into a battery’s condition and helps in predicting its performance under load. Here are some key reasons why it’s essential:
- Performance Evaluation:
- A battery with high internal resistance will struggle to deliver power efficiently. As the internal resistance increases, the battery’s voltage drops faster under load, reducing the overall energy output. By measuring internal resistance, you can assess whether the battery is still capable of meeting the demands of the device it powers.
- Health Monitoring:
- As batteries age, their internal resistance increases, which can be an early indicator of a failing cell. Regularly measuring internal resistance battery can help you monitor the health of the battery and determine when it might need replacement, preventing unexpected failures and ensuring the reliability of devices.
- Efficiency Optimization:
- Batteries with lower internal resistance are more efficient at delivering power. This means less energy is wasted as heat, and more of the energy stored in the battery is available for use. By regularly measuring internal resistance, you can optimize the efficiency of battery-operated devices and systems, saving energy and reducing operational costs.
- Safety Assurance:
- High internal resistance can cause a battery to overheat, which might lead to thermal runaway or even battery failure. By measuring internal resistance, you can detect signs of excessive resistance and prevent overheating, which could pose a safety risk, especially in applications such as electric vehicles or energy storage systems.
Methods to Measure Internal Resistance Battery
Several techniques are used to measure internal resistance. Each method has its advantages and is suitable for specific applications. Let’s explore the most common ones.
1. DC Load Method
Overview: The DC load method is one of the simplest and most widely used techniques for measuring internal resistance. It involves applying a direct current to the battery and measuring the voltage drop across it. This method is most suitable for batteries with moderate to high internal resistance.
Pros: This method is simple, inexpensive, and can be done with basic equipment like a multimeter and load resistor.
Cons: It may not be accurate for batteries with very low internal resistance, and the measurement can be affected by temperature variations.
2. AC Impedance Method
Overview: The AC impedance method involves applying an alternating current signal to the battery and measuring the impedance at various frequencies. This technique is highly accurate and can measure both the real and imaginary components of the internal resistance.
Procedure:
Use an impedance meter or specialized device to apply a small AC signal to the battery.
Measure the impedance at different frequencies. Impedance meters provide data on the resistance and reactance of the battery at various points.
Pros: This method is highly accurate and can be used to measure low internal resistance, making it ideal for high-performance batteries like those used in electric vehicles or energy storage systems.
Cons: It requires specialized equipment, making it more expensive and less accessible for casual users.
3. Hybrid Pulse Power Characterization (HPPC)
Overview: The HPPC method combines both DC and AC techniques to measure internal resistance. It involves applying a sequence of current pulses to the battery and recording the voltage and current changes during each pulse. This method provides detailed information about the battery’s dynamic behavior under load.
Procedure:
Apply a series of pulses to the battery and measure the voltage drop for each pulse.
Record the current drawn during each pulse.
Analyze the results to determine the internal resistance at various points during the test.
Pros: HPPC provides a comprehensive analysis of battery performance, including both static and dynamic resistance measurements.
Cons: The method is complex, requiring specialized equipment and more time to complete.
4. Using a Battery Internal Resistance Tester
Overview: A battery internal resistance tester is a dedicated device designed to measure the internal resistance of a battery directly. These testers use various methods, such as DC load or AC impedance, to provide accurate measurements.
Procedure:
Connect the tester to the battery terminals, ensuring proper contact with the positive and negative terminals.
Follow the device’s instructions to initiate the measurement. Most testers automatically apply the correct load and measure the voltage drop.
Obtain the result displayed on the tester’s screen, which will show the internal resistance value.
Pros: Battery internal resistance testers are fast, user-friendly, and accurate. They provide quick results without the need for complex calculations.
Cons: These testers can be expensive, especially for high-precision models.
Step-by-Step Guide to Measure Internal Resistance Battery
Prepare the Battery:
Ensure that the battery is fully charged or at a standard state of charge (SOC) to obtain an accurate measurement. Avoid measuring internal resistance when the battery is at a very low charge, as this can give misleading results.
Ensure the battery is at room temperature, as temperature can significantly affect the internal resistance.
Select the Right Method:
Choose a measurement method based on the type of battery, the accuracy required, and the equipment available. For example, the DC load method might be suitable for quick, rough measurements, while the AC impedance method is better for high-precision applications.
Gather Equipment:
Depending on the chosen method, gather the necessary tools such as a multimeter, impedance meter, load resistor, or battery internal resistance tester.
Perform the Measurement:
Carefully follow the procedure outlined for your chosen method. Ensure all connections are secure, and take multiple measurements if necessary to confirm the accuracy of the results.
Record and Analyze Results:
Compare the measured internal resistance with the battery manufacturer’s specifications or historical measurements. A significant increase in internal resistance over time could indicate that the battery is nearing the end of its lifespan.

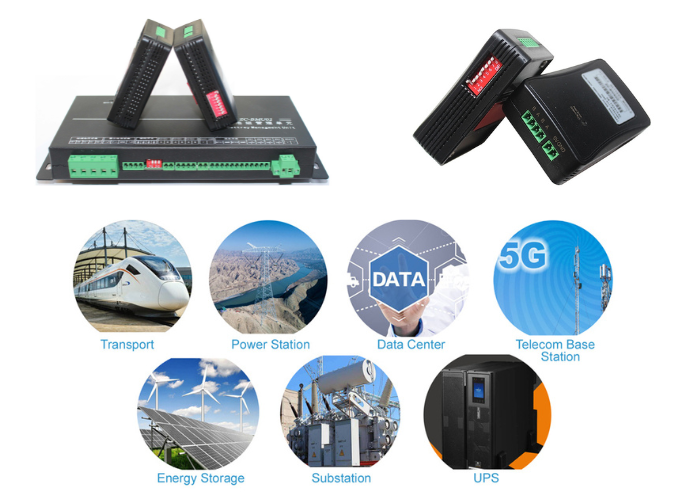
Applications of Measuring Internal Resistance Battery
Electric Vehicles (EVs):
EVs rely on large lithium-ion batteries to provide the necessary power for long-range driving. Measuring internal resistance in these batteries helps determine their health, efficiency, and remaining lifespan, ensuring that they can meet the power demands of the vehicle.
Renewable Energy Storage:
Batteries are widely used to store energy from renewable sources like solar and wind. Measuring internal resistance helps ensure that these batteries can store and release energy efficiently, reducing energy loss and improving system performance.
Consumer Electronics:
Devices like smartphones, laptops, and tablets rely on rechargeable batteries. Measuring the internal resistance of these batteries helps diagnose potential issues, such as poor battery life or charging problems, before they become critical.
Automotive Applications:
Lead-acid batteries are commonly used in vehicles for starting engines and powering accessories. Measuring the internal resistance of these batteries can help identify failing cells or provide early warning signs of potential failure, preventing breakdowns.
Common Tools for Measuring Internal Resistance
Multimeters:
Multimeters are versatile tools that can measure voltage, current, and resistance. While not the most accurate for measuring internal resistance, they can be used for quick checks in less critical applications.
These are specialized devices designed specifically for measuring the internal resistance of batteries. They are fast, easy to use, and can provide accurate results for most types of batteries.
Impedance Analyzers:
Impedance analyzers are high-precision devices that can measure both the real and imaginary components of the battery’s internal resistance. These tools are ideal for high-performance batteries, such as those used in electric vehicles.
Integrated Diagnostic Systems:
Some advanced diagnostic systems, especially in automotive and industrial applications, come with built-in internal resistance measurement capabilities. These systems provide comprehensive data on battery health, performance, and safety.
Conclusion
Measuring the internal resistance of a battery is an indispensable practice for anyone relying on batteries in their personal or professional life. By understanding how to measure internal resistance battery, you can ensure optimal performance, safety, and longevity for your energy storage systems. With proper tools, techniques, and interpretation, this process becomes a straightforward yet powerful diagnostic tool.
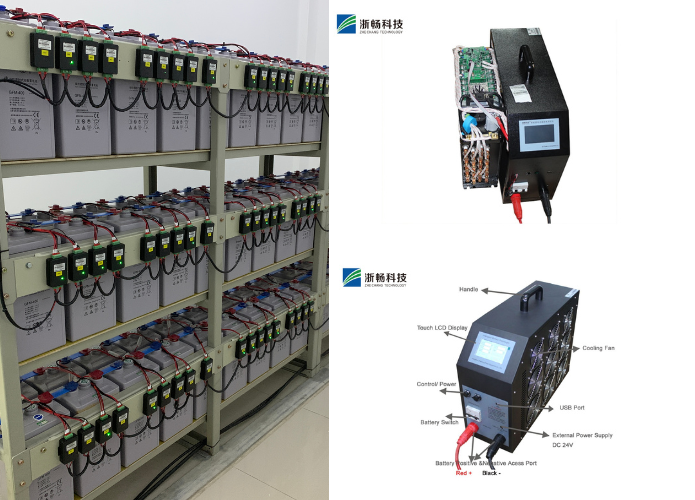
Popular Battery Tester
Popular Battery Tester
Latest News
Latest News

Get Price of Battery Tester
Get Price of Battery Tester
Address:
Floor 3, Building 1, No.1418-60, Moganshan road, Hangzhou city, Zhejiang Province, China.310015


















































