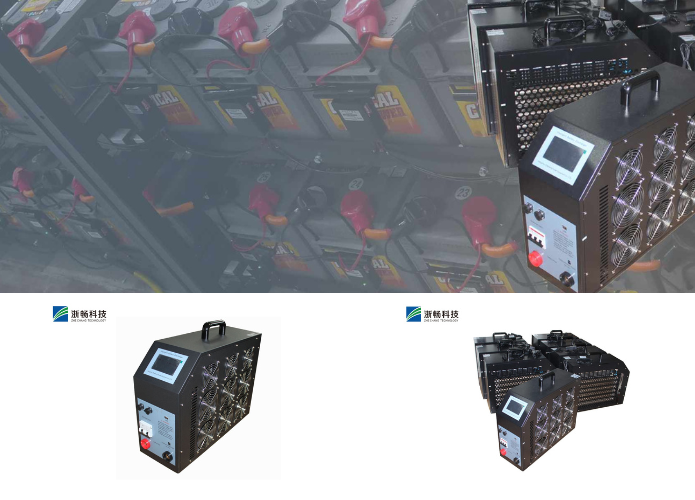
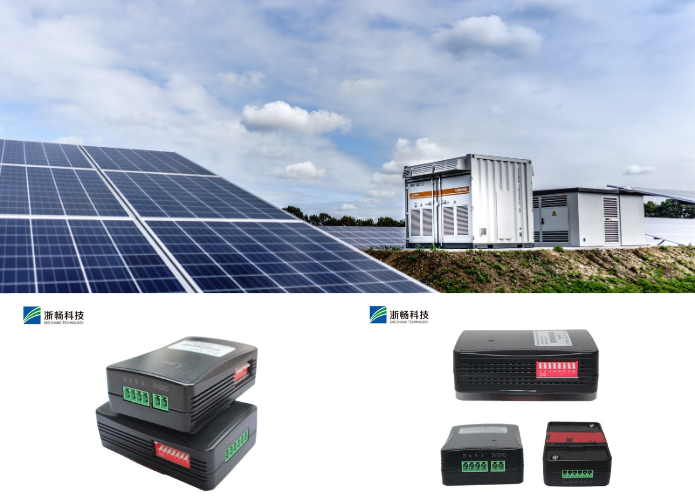
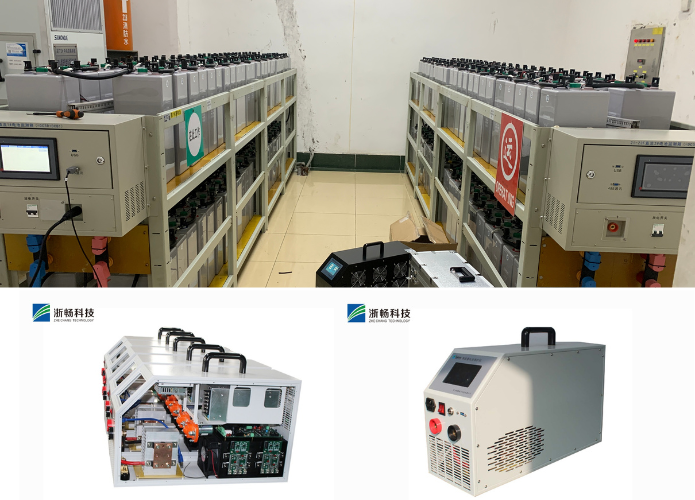
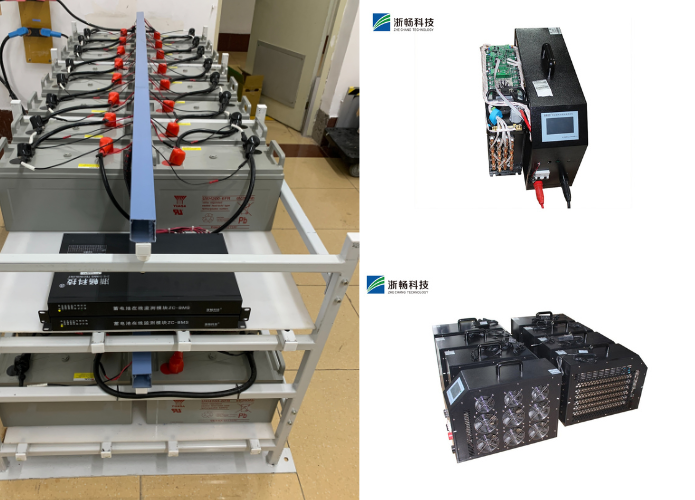
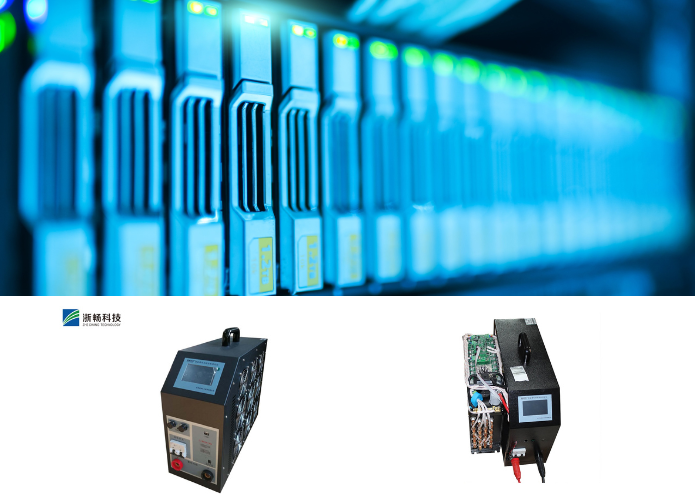
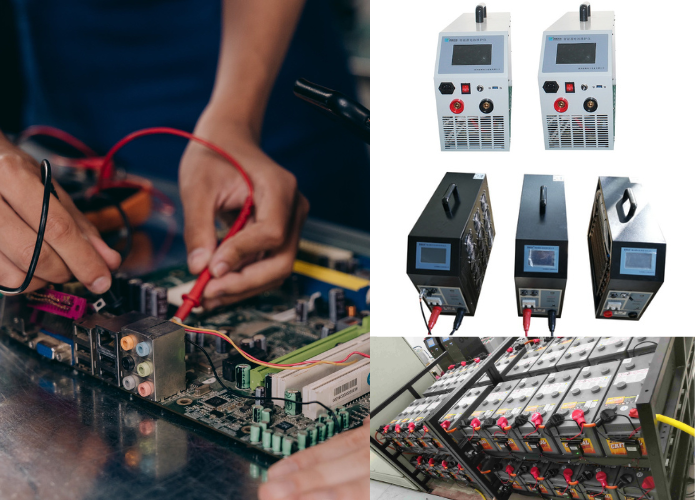
What is a Battery Discharge Tester and How Does it Work?
Battery discharge testers play a crucial role in a wide range of applications, ensuring the reliability and efficiency of battery-powered systems. In the automotive industry, they are used to evaluate the performance of car batteries, helping to prevent unexpected failures and ensuring that vehicles run smoothly. In renewable energy systems, such as solar and wind power installations, battery discharge testers are essential for monitoring the health of energy storage solutions, ensuring consistent power supply. In telecommunications, they help maintain the reliability of backup power systems, while in uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), they ensure that critical systems remain operational during power outages. Consumer electronics also benefit from battery discharge testers by guaranteeing that devices deliver the expected performance and battery life. Overall, battery discharge testers are vital tools for preventing unexpected battery failures, optimizing battery maintenance, and extending the lifespan of batteries across various industries.
What is a Battery Discharge Tester?
A battery discharge tester is an instrument designed to evaluate the capacity and performance of a battery by discharging it in a controlled manner. It applies a specific load to the battery and monitors its response, measuring parameters such as voltage, current, and temperature over time. This process helps determine the battery's health, capacity, and remaining lifespan, providing critical data for maintenance and operational efficiency. Battery discharge testers are used in various industries, including automotive, renewable energy, telecommunications, and consumer electronics, to ensure the reliability and effectiveness of battery-powered systems.
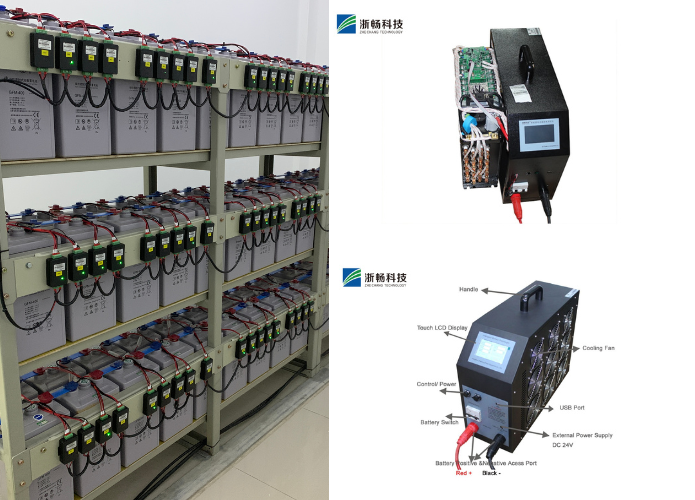
Components of a Battery Discharge Tester
1. Power Supply
The power supply in a battery discharge tester ensures that the tester itself operates correctly and can apply the necessary load to the battery being tested. It provides the energy required for the monitoring and control systems to function, ensuring accurate and consistent testing conditions.
2. Load Bank
The load bank is a critical component that applies a controlled electrical load to the battery. It simulates real-world operating conditions by drawing current from the battery, allowing the tester to measure how the battery performs under stress. Load banks can be adjustable to apply different levels of current, making it possible to test the battery's performance across a range of conditions.
3. Monitoring and Control System
The monitoring and control system oversees the entire testing process, ensuring that the discharge occurs according to predefined parameters. It continuously measures key variables such as voltage, current, and temperature, providing real-time data on the battery's performance. The control system can also adjust the load and other settings to maintain the desired test conditions, ensuring accurate and reliable results.
4. Data Logging and Display
Data logging and display components are responsible for recording and presenting the test results. The data logging system captures detailed information about the battery's performance throughout the discharge process, storing it for further analysis. The display provides a user-friendly interface, allowing operators to view real-time data and access historical test results easily. This functionality is essential for diagnosing battery health and making informed maintenance decisions.
Working Principle of a Battery Discharge Tester
1. Connection to the Battery
The battery discharge tester is connected to the battery under test through appropriate terminals or connectors. This ensures a secure electrical connection between the tester and the battery, allowing for accurate measurement and control of the discharge process.
2. Setting Discharge Parameters
* Voltage: The voltage at which the battery will be discharged is set based on the battery's specifications and the desired testing conditions. This parameter ensures that the battery is discharged to a specific voltage level to evaluate its capacity and performance accurately.
* Current: The discharge current, or load, is set to simulate real-world operating conditions. Different discharge currents may be applied to assess how the battery performs under various loads, helping to determine its capability and efficiency.
* Time Duration: The duration of the discharge test is established to monitor the battery's performance over a specific period. This parameter allows for evaluating factors such as discharge rate and capacity retention under continuous operation.
3. Initiation of the Discharge Process
Once the parameters are set, the discharge process is initiated by activating the load bank. The tester applies the preset current load to the battery, beginning the controlled discharge cycle.
4. Monitoring During Discharge
* Voltage Monitoring: Throughout the discharge process, the tester continuously monitors the battery's voltage. This helps track how the voltage level decreases as the battery discharges, providing insights into its state of charge and capacity.
* Current Monitoring: The discharge current applied to the battery is monitored to ensure it remains within the specified range. This measurement helps verify that the battery is subjected to the intended load conditions, essential for accurate performance evaluation.
* Temperature Monitoring: Temperature sensors monitor the battery's temperature during discharge. This data is crucial as temperature variations can affect battery performance and safety, allowing adjustments or alarms if the temperature exceeds safe limits.
5. Data Collection and Analysis
* Recording Performance Metrics: The tester records comprehensive performance metrics throughout the discharge test, including voltage, current, and temperature data. This information is logged in real-time, providing a detailed record of the battery's behavior under test conditions.
* Analyzing Battery Health and Capacity: After completing the discharge test, the collected data is analyzed to assess the battery's health and capacity. By comparing the initial and final voltage levels, along with discharge currents and temperature variations, the tester determines factors such as battery capacity, efficiency, and potential degradation over time. This analysis helps in making informed decisions regarding battery maintenance, replacement, or optimization strategies.

Types of Battery Discharge Testers
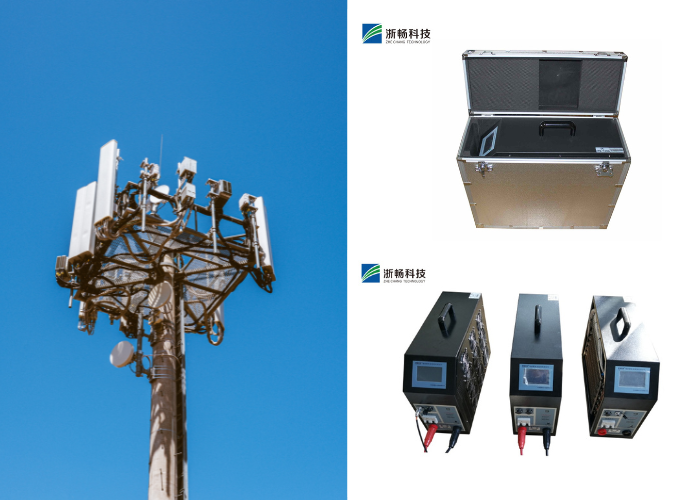
1. Portable vs. Stationary Testers
* Portable Testers: These are compact and lightweight, designed for easy transport and field use. Portable battery discharge testers are typically battery-powered themselves and are suitable for testing batteries in various locations or environments where mobility is essential.
* Stationary Testers: Stationary testers are larger and usually designed for fixed installations in laboratories or testing facilities. They are more robust and capable of handling higher currents and voltages, making them suitable for testing larger batteries or conducting extended tests under controlled conditions.
2. Manual vs. Automated Testers
* Manual Testers: Manual battery discharge testers require human intervention to adjust parameters such as voltage, current, and duration manually. Operators oversee the testing process and make adjustments based on real-time measurements and observations.
* Automated Testers: Automated battery discharge testers are equipped with programmable controllers and software interfaces that automate the entire testing process. They can set discharge parameters, initiate tests, monitor performance metrics, and analyze data without constant human oversight. Automated testers are efficient for repetitive testing and offer consistency in test conditions and results.
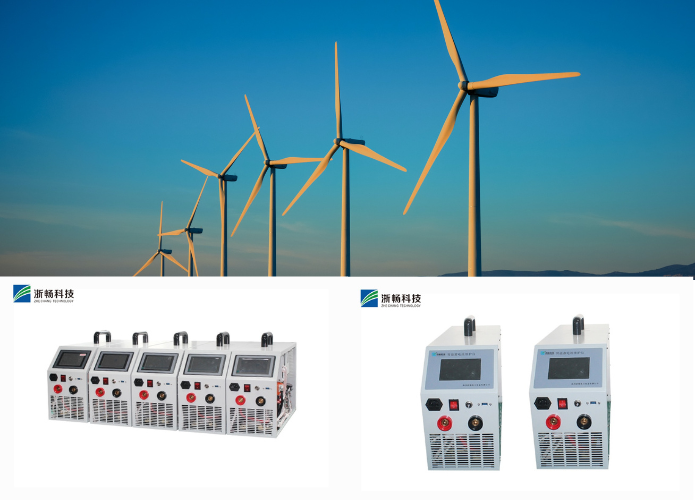
3. Single-Battery vs. Multi-Battery Testers
* Single-Battery Testers: These testers are designed to test one battery at a time. They provide detailed analysis and performance metrics for individual batteries, making them suitable for precise testing and evaluation of specific battery units.
* Multi-Battery Testers: Multi-battery testers are capable of simultaneously testing multiple batteries or battery packs. They offer scalability and efficiency, allowing operators to compare and analyze the performance of multiple batteries concurrently. This type of tester is advantageous in scenarios requiring batch testing or when evaluating batteries in parallel for consistency and performance comparison.
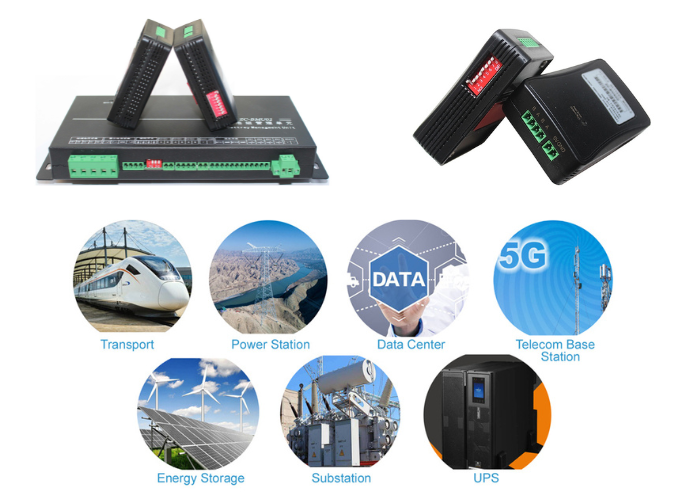
Applications of Battery Discharge Testers
1. Automotive Industry
Battery discharge testers are crucial in the automotive sector for evaluating the performance and reliability of car batteries. They ensure that batteries can start vehicles reliably in various conditions and environments. Testing helps prevent unexpected failures, ensuring optimal vehicle operation and customer satisfaction.
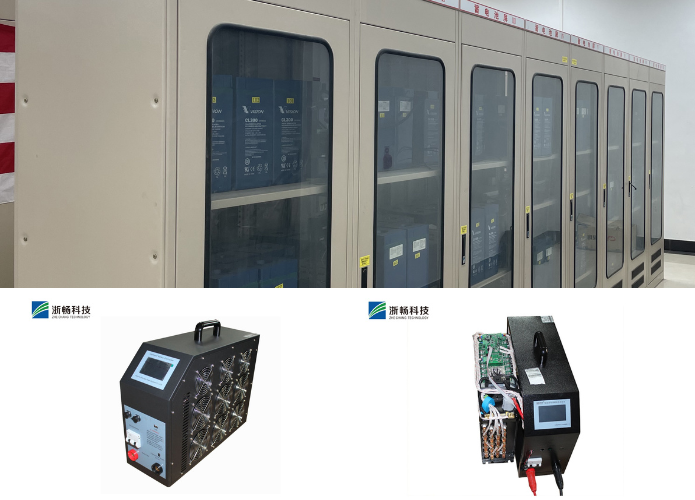
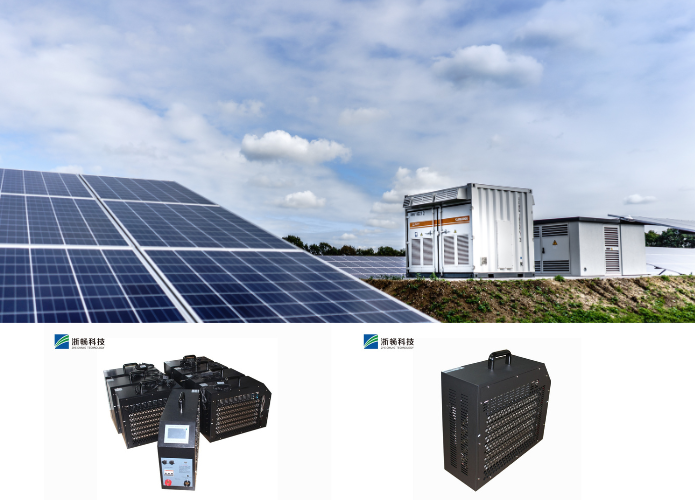
2. Renewable Energy Systems
In renewable energy applications, such as solar and wind power installations, battery discharge testers are used to assess the storage batteries' capacity and efficiency. They help maintain reliable energy storage solutions, ensuring consistent power supply during periods of low or fluctuating renewable energy generation.
3. Telecommunications
Battery backup systems are critical in telecommunications to ensure uninterrupted service during power outages. Battery discharge testers verify the performance and condition of backup batteries, ensuring they can sustain communication networks until regular power is restored. This testing is essential for reliability and compliance with service level agreements (SLAs).
4. Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS)
UPS systems provide backup power to critical equipment in data centers, hospitals, and other facilities. Battery discharge testers evaluate UPS batteries to ensure they can support equipment during power interruptions. Testing helps identify and replace weak or failing batteries before they compromise the reliability of the UPS system.
5. Consumer Electronics
Battery discharge testers are used in the consumer electronics industry to verify the performance and lifespan of batteries used in devices such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets. Testing ensures that batteries meet quality standards and deliver expected performance metrics like runtime and charging cycles. This ensures customer satisfaction and reliability of electronic devices in various applications.
Advantages of Using Battery Discharge Testers
1. Accurate Assessment of Battery Health
Battery discharge testers provide precise measurements of key performance metrics such as capacity, voltage, and current. This allows for a thorough evaluation of battery health, identifying issues like capacity degradation or internal resistance changes that may affect performance.
2. Prevention of Unexpected Battery Failures
By regularly testing batteries with discharge testers, potential issues can be detected early. This proactive approach helps prevent unexpected battery failures that could disrupt operations in critical applications such as telecommunications, data centers, and automotive systems.
3. Extension of Battery Life
Optimized testing with discharge testers helps in identifying and addressing factors that contribute to battery degradation, such as overcharging, deep discharges, or temperature extremes. By implementing preventive maintenance based on test results, battery life can be extended, reducing the frequency of replacements.
4. Cost Savings in Battery Maintenance and Replacement
Effective use of battery discharge testers reduces overall maintenance costs by minimizing the need for premature battery replacements. By identifying batteries nearing the end of their usable life or those exhibiting performance issues early on, businesses can strategically plan replacements, avoiding costly emergency replacements and downtime.
Limitations and Challenges
1. Initial Cost and Maintenance of Testers
Battery discharge testers can involve significant initial investment, especially for high-quality, automated models capable of handling complex testing requirements. Additionally, ongoing maintenance costs, including calibration and software updates, contribute to the total cost of ownership. These expenses may pose challenges for smaller organizations or those with limited budgets.
2. Potential for Human Error in Manual Testing
Manual battery discharge testing relies on human operators to set parameters, monitor results, and interpret data. This introduces the potential for errors such as incorrect parameter settings, inconsistent testing procedures, or misinterpretation of test results. Human error can compromise the accuracy and reliability of test outcomes, affecting the effectiveness of battery health assessments.
3. Calibration and Accuracy Issues
Battery discharge testers require periodic calibration to ensure accurate measurement of voltage, current, and other performance metrics. Over time, factors such as component wear, environmental conditions, or software updates can affect the tester's calibration and measurement accuracy. Addressing calibration issues promptly is crucial to maintain the reliability and validity of test results, especially in industries where precision is critical.
These limitations and challenges underscore the importance of proper training, maintenance, and quality assurance practices when using battery discharge testers. Mitigating these issues helps maximize the effectiveness and reliability of battery testing processes in various applications.
Future Trends and Innovations
1. Integration with IoT and Smart Systems
Future battery discharge testers are likely to integrate with Internet of Things (IoT) technologies and smart systems. This integration enables testers to collect real-time data from batteries remotely, facilitating continuous monitoring and predictive maintenance. IoT connectivity allows for automatic data transmission, analysis, and alerts, enhancing efficiency and responsiveness in battery management.
2. Advances in Data Analytics for Predictive Maintenance
There will be significant advancements in data analytics capabilities for battery discharge testers. Utilizing machine learning algorithms and predictive analytics, testers can analyze historical data trends, battery performance patterns, and environmental factors to predict maintenance needs accurately. Predictive maintenance strategies help anticipate and prevent battery failures, optimize maintenance schedules, and extend battery life effectively.
3. Development of More Compact and Efficient Testers
Future trends in battery discharge testing include the development of more compact and efficient testers. Advances in technology may lead to smaller, portable testers that retain high accuracy and functionality. These compact testers will offer enhanced mobility and versatility, suitable for both field and laboratory applications. Improved efficiency in testing processes will reduce testing time while maintaining precision and reliability in assessing battery health and performance.
Conclusion
Battery discharge testers play a pivotal role in ensuring the reliability, efficiency, and longevity of batteries across various industries. By accurately assessing battery health, preventing unexpected failures, extending battery life, and optimizing maintenance costs, these testers contribute significantly to the seamless operation of battery-powered systems.
As technology advances, future trends such as integration with IoT and smart systems, advancements in data analytics for predictive maintenance, and the development of more compact and efficient testers promise to further enhance the capabilities and effectiveness of battery discharge testing. These innovations will enable smarter, more proactive approaches to battery management, ultimately supporting sustainable and resilient energy solutions for the future.
In conclusion, battery discharge testers remain essential tools for maintaining the integrity and performance of batteries, ensuring continuous and reliable power supply in critical applications worldwide.
Popular Battery Tester
Popular Battery Tester
Latest News
Latest News


Get Price of Battery Tester
Get Price of Battery Tester
Address:
Floor 3, Building 1, No.1418-60, Moganshan road, Hangzhou city, Zhejiang Province, China.310015